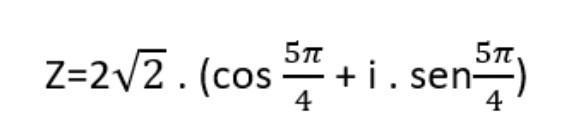Alternativa correta é a letra D.
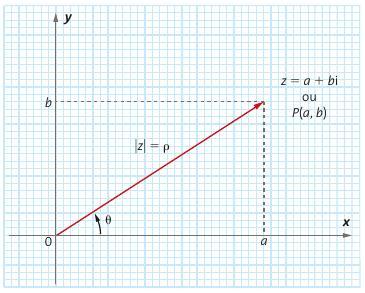
Na representação trigonométrica, um número complexo [tex]\boldsymbol{ \textstyle \sf z = a +b i }[/tex] é
determinado pelo módulo do vetor que o representa e pelo ângulo que faz com o semi-eixo positivo das abscissas.
Vide a figura em anexo:
As coordenadas cartesianas do ponto z, pode ser representado por suas coordenadas polares, que são:
- o módulo do vetor [tex]\boldsymbol{ \textstyle \sf \overrightarrow{\sf Oz }}[/tex] indicado por |z| ou [tex]\boldsymbol{ \textstyle \sf \rho }[/tex], representando a distância do ponto P à origem do plano, com [tex]\boldsymbol{ \textstyle \sf \mid z \mid \neq 0 }[/tex];
- o ângulo [tex]\boldsymbol{ \textstyle \sf \theta }[/tex], em que [tex]\boldsymbol{ \textstyle \sf 0\leq \theta \leq 2\pi }[/tex], que o vetor [tex]\boldsymbol{ \textstyle \sf \overrightarrow{\sf Oz }}[/tex] forma com o eixo x. É chamado argumento de z.
Aplicando o teorema de Pitágoras no triângulo OAP, temos:
[tex]\displaystyle \sf \mid z \mid^2 = a^2 +b^2[/tex]
[tex]\boxed{ \displaystyle \sf \mid z \mid = \rho = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} }[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf z = a +bi, \; z \neq 0[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf arg(z) = \theta[/tex]
Em trigonometria, temos:
[tex]\displaystyle \sf \cos{\theta} = \dfrac{a}{\mid z \mid } \Rightarrow a = \mid b \mid \cdot \cos{\theta}[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf \sin{\theta} = \dfrac{b}{\mid z \mid } \Rightarrow b = \mid b \mid \cdot \sin{\theta}[/tex]
Substituindo esse valores em z, temos:
[tex]\displaystyle \sf z = a +bi[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf z = \mid z \mid \cdot \cos{\theta} \: + \mid z \mid \cdot \sin{\theta} \cdot i[/tex]
[tex]\boxed{ \displaystyle \sf z = \mid z \mid \left( \cos{\theta} + i \cdot \sin{\theta} \right) }[/tex]
Chamada forma trigonométrica ou forma polar de z.
Dados fornecido pelo enunciado:
[tex]\displaystyle \sf z = 2\sqrt{2}\: \cdot \left( \cos{\dfrac{5\pi}{4}} + i \cdot \sin{ \dfrac{5 \pi}{4} } \right)[/tex]
Forma algébrica:
[tex]\displaystyle \sf \left. \begin{array}{ r r} \sf \cos{\dfrac{5\pi}{4} } = -\: \dfrac{ \sqrt{2} }{2} \\ \\ \sf \sin{\dfrac{5\pi}{4}} = -\: \dfrac{\sqrt{2} }{2} \end{array}\right \} \sf \Rightarrow \theta = 225^\circ[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf z = 2\sqrt{2}\: \cdot \left( \cos{\dfrac{5\pi}{4}} + i \cdot \sin{ \dfrac{5 \pi}{4} } \right)[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf z = 2\sqrt{2}\: \cdot \left( -\: \dfrac{ \sqrt{2} }{2} - i \cdot \dfrac{ \sqrt{2} }{2} \right)[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf z = \left( -\: \dfrac{ 2\sqrt{2}\: \cdot \sqrt{2} }{2} - i \cdot \dfrac{2\sqrt{2} \: \cdot \sqrt{2} }{2} \right)[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf z = \left( -\: \dfrac{ 2\sqrt{4}\: }{2} - i \cdot \dfrac{ 2\sqrt{4} }{2} \right)[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf z = \left( -\: \dfrac{ 2 \cdot 2 }{2} - i \cdot \dfrac{2 \cdot 2 }{2} \right)[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf z = \left( -\: \dfrac{ 4 }{2} - i \cdot \dfrac{4 }{2} \right)[/tex]
[tex]\boxed{ \boxed { \boldsymbol{ \displaystyle \sf z = -2 - 2 \cdot i }}}[/tex]
Alternativa correta é a letra D.
Mais conhecimento acesse:
https://brainly.com.br/tarefa/30354972
https://brainly.com.br/tarefa/3774743
https://brainly.com.br/tarefa/507611