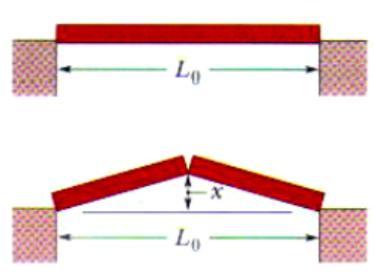
Como resultado de um aumento de temperatura de 30 C, uma barra com uma rachadura no centro dobra para cima. Se a distância fixa L é 3,0 m e o coeficiente de dilatação linear da barra é 25·10 °C , qual é a altura x do centro da barra? a) 10,0 cm b) 11,0 mm c) 11,0 m d) 5,8 cm e) 1,8 m
-
Assunto:
Física -
Autor:
carolinadawson -
Criado em:
1 ano atrás
Respostas 1
Alternativa correta é a letra D.
A dilatação Linear é o aumento de volume que acontece em apenas uma dimensão, no seu comprimento.
- O comprimento inicial (Li) é proporcional à temperatura inicial (ti);
- O comprimento final (Lf) é proporcional à temperatura final (tf);
- A dilatação linear depende do material que constitui.
A Lei da Dilatação Térmica Linear pela fórmula:
[tex]\boxed{ \boldsymbol{ \displaystyle \sf \Delta L = L_0 \cdot \alpha \cdot \Delta T }}[/tex]
Sendo que:
[tex]\textstyle \sf \Delta L \to[/tex] variação do comprimento;
[tex]\textstyle \sf L_0 \to[/tex] comprimento inicial;
[tex]\textstyle \sf \alpha \to[/tex] coeficiente de dilatação linear;
[tex]\textstyle \sf \Delta T \to[/tex] variação de temperatura.
Dados fornecidos pelo enunciado:
[tex]\displaystyle \sf \begin{cases} \sf \Delta T = 30^\circ C \\ \sf L_0 = 3,0\:m \\ \sf \alpha= 25 \cdot 10^{-6}\:^\circ C \\\sf x = \:?\: m \end{cases}[/tex]
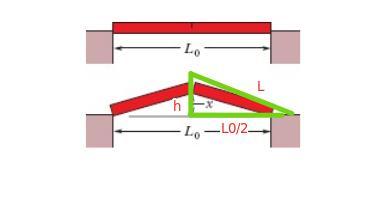
A metade da barra do comprimento original é [tex]\boldsymbol{ \textstyle \sf \ell_0 = L_0/2 }[/tex] é e o comprimento após o aumento de temperatura é [tex]\boldsymbol{ \textstyle \sf \ell = \ell_0 + \ell_0 \cdot \alpha \cdot \Delta T }[/tex].
Aplicando o teorema de Pitágoras, ( Vide a figura em anexo ), temos:
[tex]\displaystyle \sf ( \ell)^2 = (\ell_0)^2 + (x)^2[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf ( \ell)^2 - (\ell_0)^2 = x^{2}[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf x^{2} = ( \ell)^2 - (\ell_0)^2[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf x^{2} =\left(\ell_0 + \ell_0 \cdot \alpha \cdot \Delta T\right )^2 - \left ( \dfrac{\ell_0}{2} \right )^2[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf x^{2} = \ell_0^2 + 2\cdot \ell_0 \cdot \ell_0 \cdot \alpha \cdot \Delta T+ \ell_0^2 \cdot \alpha^2 \cdot \Delta T^2 - \ell_0^2[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf x^{2} = \ell_0^2 + 2\cdot \ell_0^2 \cdot \alpha \cdot \Delta T+ \ell_0^2 \cdot \alpha^2 \cdot \Delta T^2 - \ell_0^2[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf x^{2} = \ell_0^2 \cdot \left (1 + 2 \cdot \alpha \cdot \Delta T+ \alpha^2 \cdot \Delta T^2 \right ) - \ell_0^2[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf x^{2} = \ell_0^2 \cdot \left (1 + 2 \cdot \alpha \cdot \Delta T+ \underbrace{ \sf \alpha^2 \cdot \Delta T^2 }_{\sf despreza} \right ) - \ell_0^2[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf x^{2} = \ell_0^2 \cdot \left (1 + 2 \cdot \alpha \cdot \Delta T \right ) - \ell_0^2[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf x^{2} = \diagup\!\!\!{ \ell_0^2 } + 2 \cdot \ell_0^2 \cdot \alpha \cdot \Delta T - \diagup\!\!\!{ \ell_0^2}[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf x^{2} = 2 \cdot \ell_0^2 \cdot \alpha \cdot \Delta T[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf x = \sqrt{ \sf 2 \cdot \ell_0^2 \cdot \alpha \cdot \Delta T}[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf x = \ell_0 \cdot \sqrt{ \sf 2 \cdot \alpha \cdot \Delta T}[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf x = \dfrac{L_0}{2} \cdot \sqrt{ \sf 2 \cdot 25 \cdot 10^{-6} \cdot 30}[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf x = \dfrac{3,0}{2} \cdot \sqrt{ \sf 1 ,5 \cdot 10^{-3} }[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf x = 1,5 \cdot \sqrt{ \sf 1 ,5 \cdot 10^{-3} }[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \sf x = 0,058\: m[/tex]
[tex]\boxed{ \boxed { \boldsymbol{ \displaystyle \sf x = 5,8\: cm }}}[/tex]
Alternativa correta é a letra D.Mais conhecimento acesse:
https://brainly.com.br/tarefa/48090509
https://brainly.com.br/tarefa/48573302
brainly.com.br/tarefa/3886677
-
Autor:
devin633
-
Avalie uma resposta:
5